When it comes to eye health, distinguishing between similar conditions like blepharitis vs chalazion is essential. Both involve the eyelids and can cause discomfort, but they stem from different causes and require unique approaches to treatment.
This blog dives deep into blepharitis vs chalazion, helping you understand their differences, symptoms, and management strategies. By the end, you’ll have a clear grasp of these conditions and know how to take better care of your eyes.
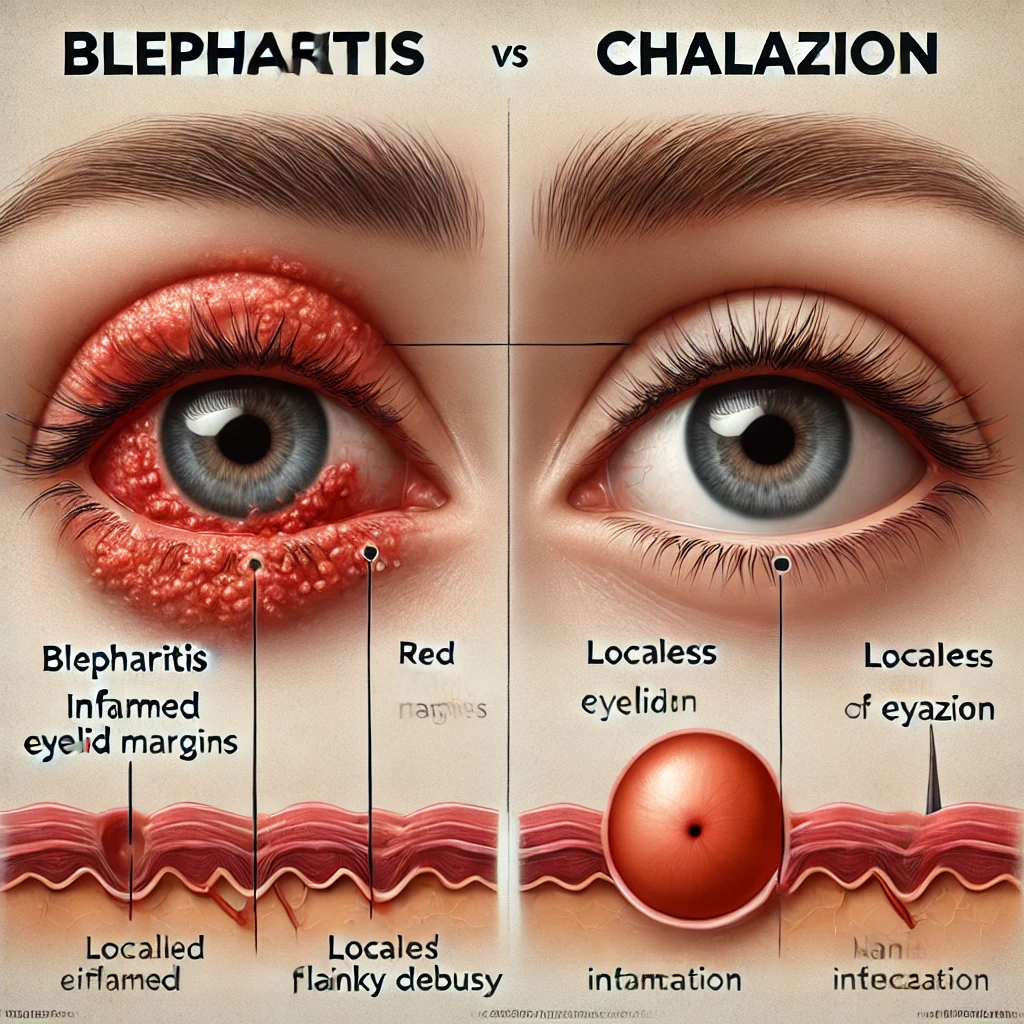
What Is Blepharitis? Key Facts to Know
Blepharitis is a common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelid edges. It commonly develops due to blocked oil glands located at the base of the eyelashes.
Key symptoms include redness, itchiness, flaking skin, and crusting along the lash line. While blepharitis isn’t contagious, it can be persistent and challenging to manage without proper care.
Blepharitis can be divided into two main categories: anterior blepharitis, which affects the outer edge of the eyelid where eyelashes are located, and posterior blepharitis,
which involves the inner edge of the eyelid that interconnected to the eye surface. Poor eyelid hygiene and conditions like rosacea or dandruff can contribute to its development.
Chalazion Explained:
A chalazion is a lump or bump that develops on the eyelid, usually caused by a blocked meibomian gland. Chalazion vs stye, in the stye which is painful and caused by infection, a chalazion is typically painless. Over time, it can grow larger and cause pressure on the eye, potentially affecting vision.
Although chalazions are not usually harmful, they can become bothersome. They often resolve on their own, but persistent cases may require treatment. Good eyelid hygiene is crucial to prevent their occurrence.
Comparing Symptoms: Blepharitis vs Chalazion
When discussing blepharitis vs chalazion, the symptoms are where distinctions become clear:
- Blepharitis Symptoms: Redness, itchiness, burning sensation, crusty eyelids, and sensitivity to light. The condition that effects both eyes and also related to chronic conditions.
- Chalazion Symptoms: A localized lump or bump, mild tenderness (in some cases), and occasional vision blurring if the bump presses on the eye.
Understanding the Causes of Blepharitis
Blepharitis vs chalazion, blepharitis is often associated with bacterial infections, skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, or dysfunction of the meibomian glands. These glands, found in the eyelids, secrete oils that keep the eyes moisturized. When these glands become blocked or inflamed, blepharitis can occur.
Other contributing factors include:
- Allergies
- Poor eyelid hygiene
- Overgrowth of bacteria near the eyelashes
What Causes a Chalazion to Develop?
Blepharitis vs Chalazions, chalazion is the abnormality or condition that occurs in eyes due to the blockage of meibomian glands. Unlike a stye, a chalazion doesn’t result from an infection. Factors that increase the risk of developing a chalazion include:
- Chronic blepharitis
- Acne or rosacea
- Previous history of chalazions
- Poor eyelid hygiene
Regular cleaning of the eyelids can reduce the risk of gland blockages and chalazion formation.
Diagnosis: How to Differentiate Blepharitis vs Chalazion
An eye doctor will typically examine your eyelids and ask about symptoms to determine if you have blepharitis or a chalazion. Blepharitis usually involves widespread inflammation, whereas a chalazion is a distinct lump.
The presence of crusting, flaking, or redness around the lashes often points to blepharitis. A localized bump, especially one that feels firm and painless, is more indicative of a chalazion.
Treatment Options for Blepharitis
Treating blepharitis typically requires a mix of good eyelid hygiene practices and appropriate medical therapies:
- Warm Compresses: Help loosen crusts and unblock oil glands.
- Eyelid Scrubs: Using a gentle cleanser to remove debris and bacteria.
- Medications: Antibiotic ointments or drops and, in some cases, steroid drops to reduce inflammation.
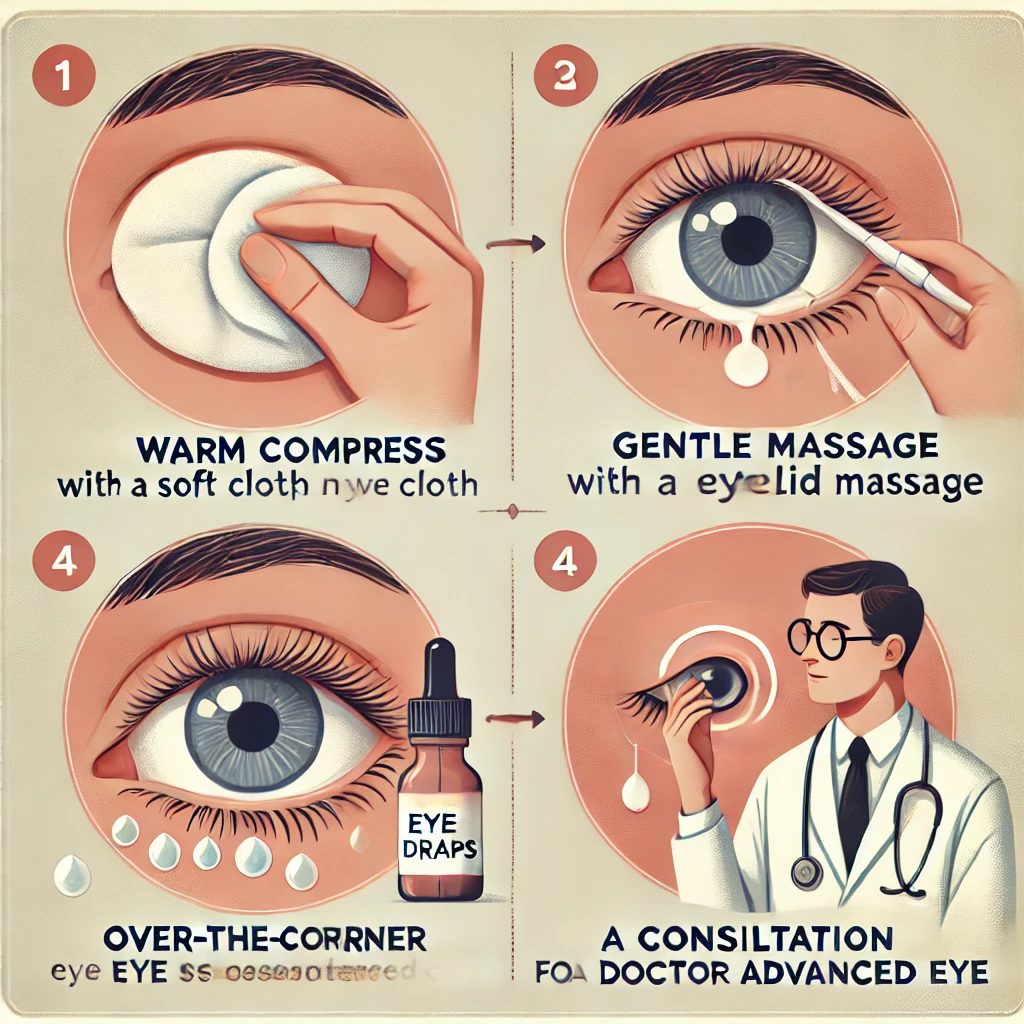
Effective Ways to Treat Chalazion
Most chalazions resolve without medical intervention, but there are steps you can take to speed up the process:
- Gentle Massage: Using clean fingers to massage the eyelid may help drain the gland.
- Medical Intervention: If a chalazion doesn’t improve, your doctor might drain it or prescribe corticosteroid injections.
- Warm Compresses: Place a warm cloth over your eyelids for 10-15 minutes multiple times a day to help dissolve the buildup.
Blepharitis Prevention: Tips for Long-Term Relief
Preventing blepharitis involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene:
- Wash your eyes and specifically eyelid with cleaner.
- Keep your hands away from your eyes unless they are clean.
- Address underlying issues such as rosacea or dandruff to help control symptoms.
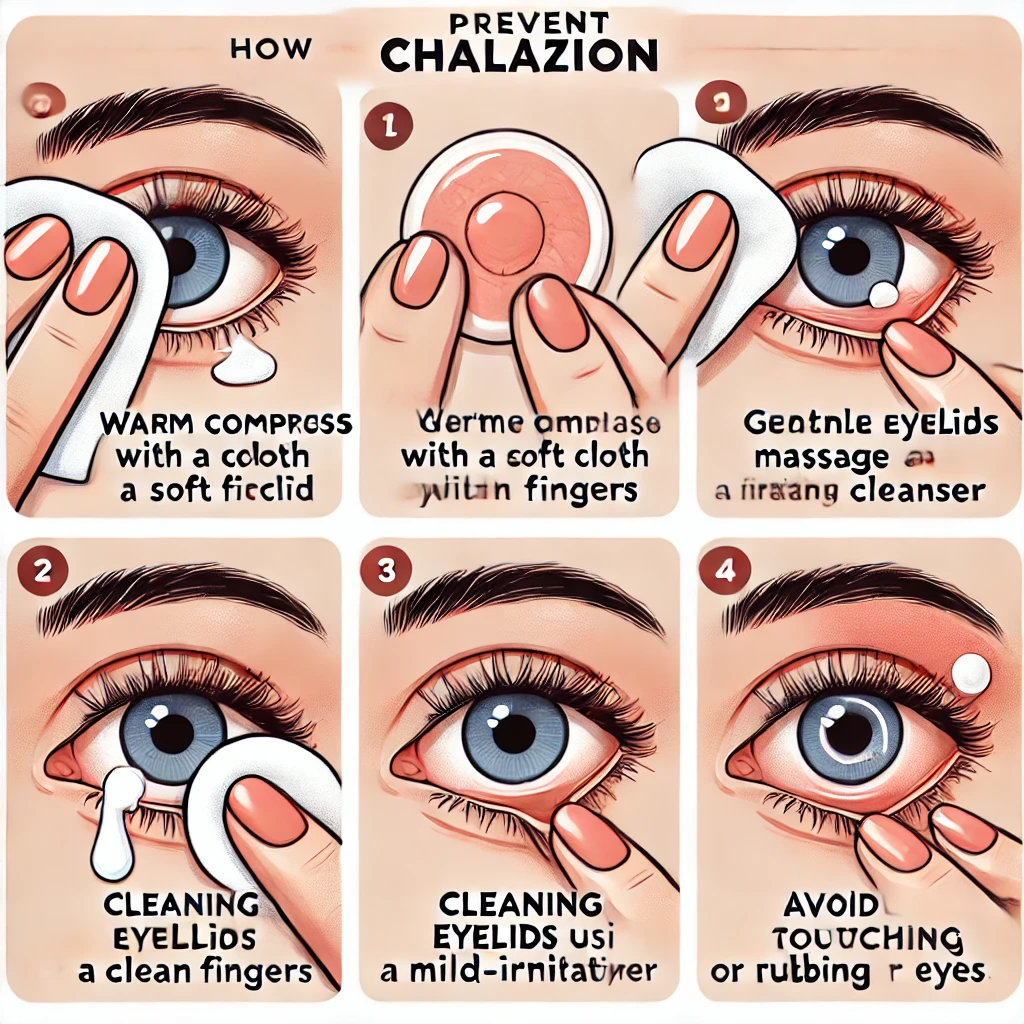
How to Prevent Chalazion:
Preventing a chalazion requires regular care:
- Clean your eyelids to prevent oil gland blockages.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes if your hands haven’t been washed.
- Treat underlying conditions like blepharitis to minimize your risk.
Lifestyle changes, such as managing stress and eating a balanced diet, can also contribute to healthier eyes.
Complications of Blepharitis vs Chalazion
Although usually manageable, both conditions Blepharitis vs chalazion can lead to complications:
- Blepharitis: Chronic cases may result in eyelash loss, scarring of the eyelids, or secondary infections.
- Chalazion: Large or untreated chalazions may cause astigmatism or vision blurring due to pressure on the cornea.
When to Seek Medical Help for Eye Issues
While home remedies are often effective, some situations require a doctor’s attention:
- Blepharitis symptoms persist despite proper care.
- A chalazion grows rapidly or becomes painful.
- Vision changes or excessive eye discharge occur.
What is the difference between blepharitis vs chalazion?
Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelid, often involving redness, itching, and crusting. A chalazion is a lump that forms when a meibomian gland becomes blocked, typically painless and firm.
Can blepharitis turn into a chalazion?
Yes, chronic blepharitis can lead to blocked meibomian glands, which may result in chalazion formation.
Are blepharitis and chalazion contagious?
No, neither blepharitis nor chalazions are contagious.
How do you treat blepharitis?
Treatment includes warm compresses, eyelid scrubs, and antibiotics in some cases.
What is the best treatment for a chalazion?
Warm compresses are the first line of treatment. If it doesn’t resolve, a doctor may drain it or recommend corticosteroid injections.
Can you prevent blepharitis?
Yes, practicing good eyelid hygiene and managing underlying conditions can help prevent blepharitis.
